-
Home
-
Product
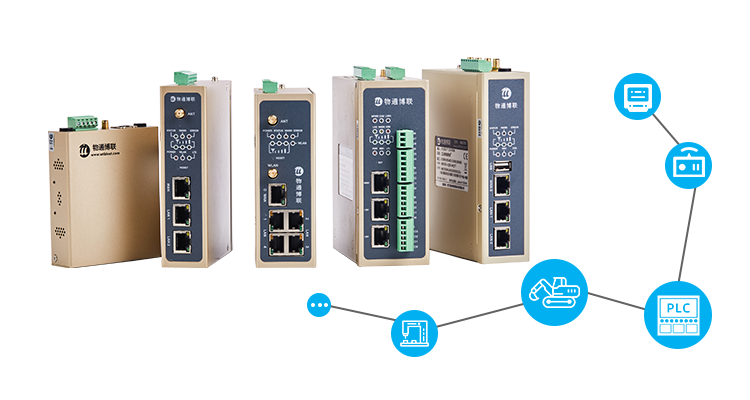
Product Wutong Bolian · WG series industrial intelligent gateway is a high reliability industrial intelligent gateway that supports the collection of data of various industrial equipment such as PLC, instrument, water environmental protection, power equipment, CNC, and has protocol analysis and edge computing. It is the core edge node for building industrial Internet system.View details>Equipment NetworkData CollectionProtocol AnalysisEdge ComputingCloud AccessOpen Interface
Wutong Bolian · WG series industrial intelligent gateway is a high reliability industrial intelligent gateway that supports the collection of data of various industrial equipment such as PLC, instrument, water environmental protection, power equipment, CNC, and has protocol analysis and edge computing. It is the core edge node for building industrial Internet system.View details>Equipment NetworkData CollectionProtocol AnalysisEdge ComputingCloud AccessOpen Interface -
Solution
SolutionFactory line IOT system Remote Monitoring of Pumping Station Rural Sewage Monitoring Smart Heating System Oilfield IoT System Equipment Remote Maintenance Smart Breeding System Intelligent Microgrid System On the basis of digital factory, with the purpose of optimizing production process and business operation, intelligent factory uses Internet of Things technology and monitoring technology to strengthen information management services, improve the controllability of production process, reduce manual intervention of production line, reasonably plan scheduling, realize information unification, group unified monitoring, realize product life cycle and spare parts management, and improve the intelligent degree of manufacturing factory, Reduce operation and maintenance costs and promote industrial upgrading of enterprises.View details>Equipment interconnectionEquipment data collectionEquipment data standardizationRemote Maintenance of equipmentProduction line data visualizationProduction line data analysis
On the basis of digital factory, with the purpose of optimizing production process and business operation, intelligent factory uses Internet of Things technology and monitoring technology to strengthen information management services, improve the controllability of production process, reduce manual intervention of production line, reasonably plan scheduling, realize information unification, group unified monitoring, realize product life cycle and spare parts management, and improve the intelligent degree of manufacturing factory, Reduce operation and maintenance costs and promote industrial upgrading of enterprises.View details>Equipment interconnectionEquipment data collectionEquipment data standardizationRemote Maintenance of equipmentProduction line data visualizationProduction line data analysis -
About Us
About Us Wutong Bolian, founded in 2011, is a professional provider of industrial Internet of Things products and industrial digital solutions. Wutong Bolian focuses on providing industrial intelligent gateway, industrial data acquisition terminal, equipment remote maintenance management system, industrial equipment data cloud platform and other products and solutions for equipment manufacturers, intelligent factories, industrial projects and other fields, to help customers achieve digital operation management and industrial Internet new value mining. Wutong Bolian's products are widely used in intelligent factories, equipment manufacturers, environmental protection industry, energy industry, municipal engineering, industrial automation, smart agriculture, building intelligence and other industrial fields.View details>
Wutong Bolian, founded in 2011, is a professional provider of industrial Internet of Things products and industrial digital solutions. Wutong Bolian focuses on providing industrial intelligent gateway, industrial data acquisition terminal, equipment remote maintenance management system, industrial equipment data cloud platform and other products and solutions for equipment manufacturers, intelligent factories, industrial projects and other fields, to help customers achieve digital operation management and industrial Internet new value mining. Wutong Bolian's products are widely used in intelligent factories, equipment manufacturers, environmental protection industry, energy industry, municipal engineering, industrial automation, smart agriculture, building intelligence and other industrial fields.View details> -
Service Support
-
Link Us